The liver is among the vital organs of the human body. It is responsible for metabolism, detoxification, the production of bile, and the storage of nutrients. If the liver is affected by illness, it affects the general health of a person in a major way. In the list of prevalent liver diseases, fatty liver, hepatitis, and cirrhosis are the most prevalent. Knowing their causes as well as symptoms and treatments is vital for better management and prevention.
What are Liver Disorders?
Liver disorders refer to medical conditions that impact the normal function that the liver. They can be mildly inflamed to chronically, severely damaged, which leads to the failure of the liver. The most frequently reported liver problems are:
-
Fatty Liver Disease
-
Hepatitis (A, B, C, etc.)
-
Cirrhosis
Fatty Liver Disease

Overview
Fatty liver disease is a condition that occurs when fat builds up within liver cells. It is divided into two categories:
-
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD)—caused by excessive consumption of alcohol.
-
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)—occurs in those who drink very little or no alcohol.
Causes
-
Obesity
-
Diabetes
-
High cholesterol
-
Lifestyle of sedentary
-
Excessive alcohol intake
Symptoms
-
Most often, symptoms are evident in the beginning stages.
-
Fatigue
-
Abdominal discomfort
-
The larger the liver (in the advanced stage)
Treatment
-
Lifestyle adjustments (diet and exercise, and weight loss)
-
Reduced consumption of alcohol
-
Medicines for related diseases (diabetes, cholesterol)
-
Monitoring of the liver’s health regularly
Hepatitis
Overview
Hepatitis is a term used to describe liver inflammation that is often due to viral infection but can also result from alcohol, toxins, or autoimmune disorders.
Types
-
Hepatitis A is spread through contaminated food items and drinking water
-
Hepatitis B—transmitted through blood and bodily fluids
-
Hepatitis C is most often spread through infected blood
-
Hepatitis D & E are less prevalent but still very dangerous
Symptoms
-
Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes)
-
Fatigue
-
Abdominal pain
-
Urine that is dark
-
A loss of appetite
Treatment
-
Hepatitis A & E is usually self-limiting. needing support
-
Hepatitis B & C Antiviral drugs and long-term monitoring
-
There is a vaccine available to treat Hepatitis A and B.
-
Beware of alcohol, eat the right diet, and ensure good hygiene
Cirrhosis
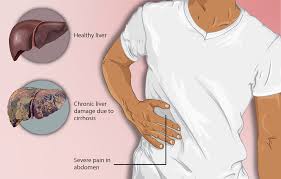
Overview
Cirrhosis is the process of scarring the liver caused by chronic liver damage. It’s usually caused by the long-term use of alcohol, hepatitis infection, or an untreated fatty liver.
Causes
-
Consumption of alcohol in the long term
-
Hepatitis chronically viral infection (especially B & C)
-
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
-
Genetic liver disorders
Symptoms
-
Fatigue
-
The bleeding and bruises are easy to treat.
-
Jaundice
-
Ascites (fluid buildup in the abdomen)
-
Confusing (hepatic encephalopathy)
Treatment
-
There is no cure that is 100% complete once you have it.
-
Lifestyle modification (alcohol cessation, healthy diet)
-
Medicines to treat complications
-
Liver transplants in extreme instances
Prevention of Liver Disorders
-
Maintain a healthy weight
-
Consume a balanced and healthy diet
-
Exercise regularly
-
Avoid excessive alcohol
-
Be vaccinated for Hepatitis A and B.
-
A regular liver function test is recommended if you are at risk
Conclusion
The liver plays an important role in maintaining the health of your body. Diseases such as fatty liver, hepatitis, and cirrhosis could lead to serious complications if not treated. Early detection, as well as preventive measures and lifestyle modifications, can safeguard the liver and boost overall wellness. Consulting a professional gastroenterologist specialist or hepatologist is crucial for an appropriate treatment of liver disorders.

